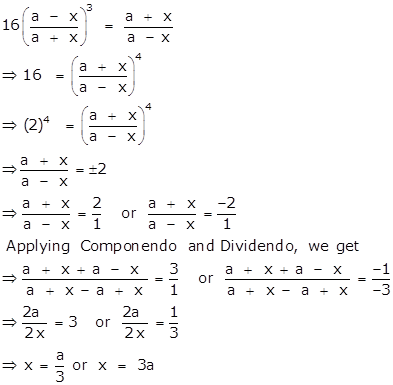Class 10 SELINA Solutions Maths Chapter 7 - Ratio and Proportion (Including Properties and Uses)
Solutions play a pivotal role in the academic journey of all students. They allow students to understand and master concepts covered in their curriculum. Students can learn, understand, and clarify doubts and use solutions to make notes and revise important concepts.
Selina Solutions are the ultimate go-to resource for ICSE students. These solutions provide in-depth knowledge and step-by-step explanations so that students can better comprehend and retain the concepts. With easy-to-understand language and illustrative examples, it offers the correct approach to solving mathematical problems.
The solutions cover all the topics and concepts in ICSE Class 10 Math syllabus, including Ratios and Proportions. It explains the properties of ratios and proportions, the concept of equivalent ratios, the multiplication and division of ratios, and cross-multiplication. Detailed explanations help students understand the logic and apply it to different questions. These solutions are designed in alignment with the ICSE exam pattern and marking scheme. Using these solutions, students can self-assess, evaluate their understanding, track their progress, and identify improvement areas. Therefore, students prepare effectively and improve their scores.
Topper Learning provides Selina Solutions for classes 9 and 10 for Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Maths. We aim to empower students through our online education platform. In order to do so, we provide several resources such as textbook solutions, sample papers, video lessons, revision notes, important questions, mock tests, and much more. Therefore, we enable them to excel in their ICSE exams and build a strong foundation for higher education.
Ratio and Proportion (Including Properties and Uses) Exercise Ex. 7(A)
Solution 1
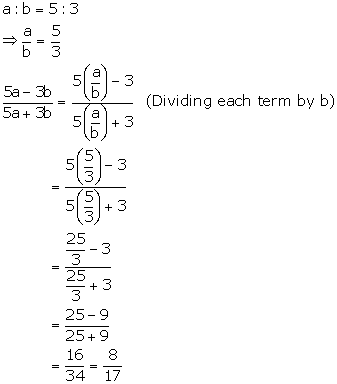
Solution 2

Solution 3
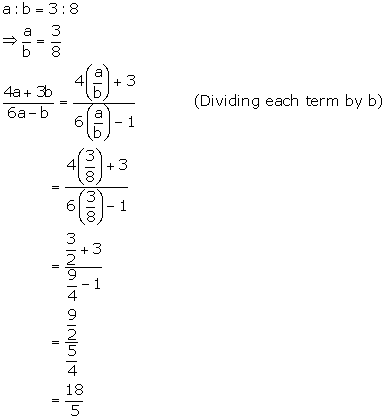
Solution 4
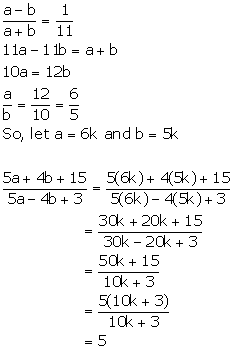
Hence, (5a + 4b + 15): (5a - 4b + 3) = 5: 1
Solution 5
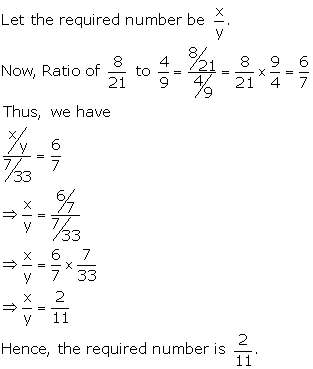
Solution 6
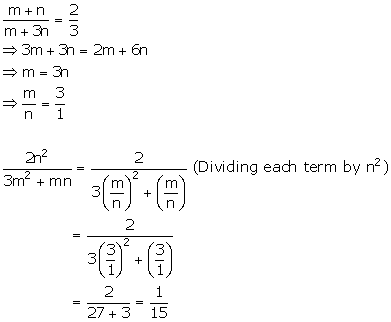
Solution 7
x2 + 6y2 = 5xy
Dividing both sides by y2, we get,
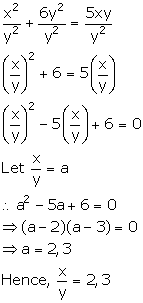
Solution 8
Given,
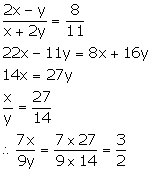
Solution 9
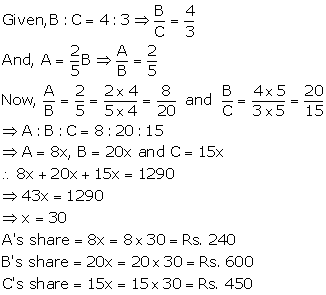
Solution 10
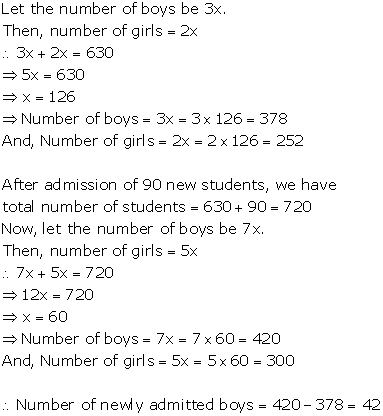
Solution 11
Let x be subtracted from each term of the ratio 9: 17.
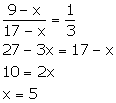
Thus, the required number which should be subtracted is 5.
Solution 12

Solution 13
Assuming that all the men do the same amount of work in one day and one day work of each man = 1 units, we have,
Amount of work done by (x - 2) men in (4x + 1) days
= Amount of work done by (x - 2)(4x + 1) men in one day
= (x - 2)(4x + 1) units of work
Similarly,
Amount of work done by (4x + 1) men in (2x - 3) days
= (4x + 1)(2x - 3) units of work
According to the given information,
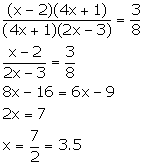
Solution 14
According to the given information,
Increased (new) bus fare = ![]() original bus fare
original bus fare
(i) We have:
Increased (new) bus fare = ![]() Rs 245 = Rs 315
Rs 245 = Rs 315
![]() Increase in fare = Rs 315 - Rs
245 = Rs 70
Increase in fare = Rs 315 - Rs
245 = Rs 70
(ii) We have:
Rs 207 = ![]() original bus fare
original bus fare
Original bus fare = ![]()
![]() Increase in fare = Rs 207 - Rs
161 = Rs 46
Increase in fare = Rs 207 - Rs
161 = Rs 46
Solution 15
Let the cost of the entry ticket initially and at present be 10 x and 13x respectively.
Let the number of visitors initially and at present be 6y and 5y respectively.
Initially, total collection = 10x ![]() 6y = 60 xy
6y = 60 xy
At present, total collection = 13x
![]() 5y = 65 xy
5y = 65 xy
Ratio of total collection = 60 xy: 65 xy = 12: 13
Thus, the total collection has increased in the ratio 12: 13.
Solution 16
Let the original number of oranges and apples be 7x and 13x.
According to the given information,
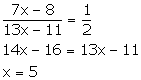
Thus, the original number of
oranges and apples are 7 ![]() 5 = 35 and 13
5 = 35 and 13 ![]() 5 = 65 respectively.
5 = 65 respectively.
Solution 17

Solution 18
(A)
(i)
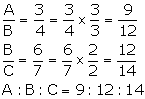
(ii)
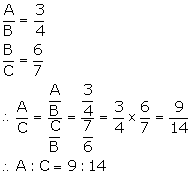
(B)
(i)
Solution 19(i)
3A = 4B = 6C
3A = 4B ![]()
4B = 6C ![]()
Hence, A: B: C = 4: 3: 2
Solution 19(ii)
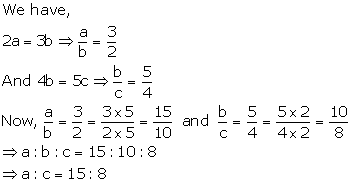
Solution 20
(i) Required compound ratio = 2 ![]() 9
9 ![]() 14: 3
14: 3 ![]() 14
14 ![]() 27
27
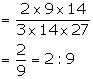
(ii) Required compound ratio = 2a ![]() mn
mn![]() x: 3b
x: 3b ![]() x2
x2![]() n
n
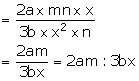
(iii) Required compound ratio = ![]()
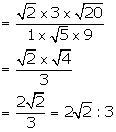
Solution 21
(i) Duplicate ratio of 3: 4 = 32: 42 = 9: 16
(ii) Duplicate ratio of ![]()
Solution 22
(i) Triplicate ratio of 1: 3 = 13: 33 = 1: 27
(ii) Triplicate ratio of ![]()

Solution 23
(i) Sub-duplicate ratio of 9: 16 =
![]()
(ii) Sub-duplicate ratio of(x - y)4: (x + y)6
= ![]()
Solution 24
(i) Sub-triplicate ratio of 64: 27
= ![]()
(ii) Sub-triplicate ratio of x3:
125y3 = ![]()
Solution 25
(i) Reciprocal ratio of 5: 8 = ![]()
(ii) Reciprocal ratio of 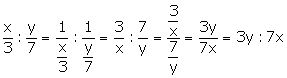
Solution 26

Solution 27
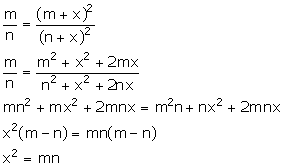
Solution 28

Solution 29
Reciprocal ratio of 15: 28 = 28: 15
Sub-duplicate ratio of 36: 49 = ![]()
Triplicate ratio of 5: 4 = 53: 43 = 125: 64
Required compounded ratio
= ![]()
Solution 30(a)
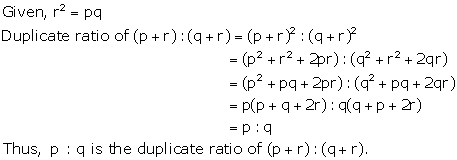
Solution 30(b)
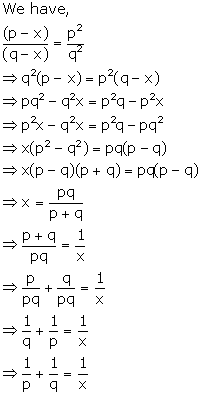
Ratio and Proportion (Including Properties and Uses) Exercise Ex. 7(B)
Solution 1
(i) Let the fourth proportional to 1.5, 4.5 and 3.5 be x.
![]() 1.5 : 4.5 = 3.5 : x
1.5 : 4.5 = 3.5 : x
![]() 1.5
1.5 ![]() x = 3.5
x = 3.5 ![]() 4.5
4.5
![]() x = 10.5
x = 10.5
(ii) Let the fourth proportional to 3a, 6a2 and 2ab2 be x.
![]() 3a : 6a2 = 2ab2 : x
3a : 6a2 = 2ab2 : x
![]() 3a
3a ![]() x = 2ab2
x = 2ab2![]() 6a2
6a2
![]() 3a
3a ![]() x = 12a3b2
x = 12a3b2
![]() x = 4a2b2
x = 4a2b2
Solution 2
(i)
Let the third proportional to 2![]() and 4 be x.
and 4 be x.
![]() 2
2![]() , 4, x are in
continued proportion.
, 4, x are in
continued proportion.
![]() 2
2![]() : 4 = 4 : x
: 4 = 4 : x
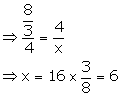
(ii) Let the third proportional to a - b and a2 - b2 be x.
![]() a - b, a2
- b2, x are in continued proportion.
a - b, a2
- b2, x are in continued proportion.
![]() a - b : a2
- b2 = a2 - b2 : x
a - b : a2
- b2 = a2 - b2 : x
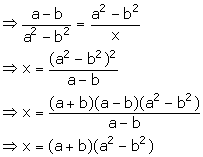
Solution 3
(i) Let the mean proportional between 6 + 3![]() and 8 - 4
and 8 - 4![]() be x.
be x.
![]() 6 + 3
6 + 3![]() , x and 8 - 4
, x and 8 - 4![]() are in continued proportion.
are in continued proportion.
![]() 6 + 3
6 + 3![]() : x = x : 8 - 4
: x = x : 8 - 4![]()
![]() x
x ![]() x = (6 + 3
x = (6 + 3![]() ) (8 - 4
) (8 - 4![]() )
)
![]() x2 = 48 + 24
x2 = 48 + 24![]() - 24
- 24![]() - 36
- 36
![]() x2 = 12
x2 = 12
![]() x= 2
x= 2![]()
(ii) Let the mean proportional between a - b and a3 - a2b be x.
![]() a - b, x, a3 - a2b are in continued proportion.
a - b, x, a3 - a2b are in continued proportion.
![]() a - b : x = x : a3 - a2b
a - b : x = x : a3 - a2b
![]() x
x ![]() x = (a - b) (a3 - a2b)
x = (a - b) (a3 - a2b)
![]() x2 = (a - b) a2(a - b) = [a(a - b)]2
x2 = (a - b) a2(a - b) = [a(a - b)]2
![]() x = a(a - b)
x = a(a - b)
Solution 4
Given, x + 5 is the mean proportion between x + 2 and x + 9.
![]() (x + 2), (x + 5) and (x + 9) are in continued proportion.
(x + 2), (x + 5) and (x + 9) are in continued proportion.
![]() (x + 2) : (x + 5) = (x + 5) : (x + 9)
(x + 2) : (x + 5) = (x + 5) : (x + 9)
![]() (x + 5)2 = (x + 2)(x + 9)
(x + 5)2 = (x + 2)(x + 9)
![]() x2 + 25 + 10x = x2 + 2x + 9x + 18
x2 + 25 + 10x = x2 + 2x + 9x + 18
![]() 25 - 18 = 11x - 10x
25 - 18 = 11x - 10x
![]() x = 7
x = 7
Solution 5
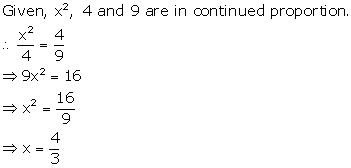
Solution 6
Let the number added be x.
![]() (6 + x) : (15
+ x) :: (20 + x) (43 + x)
(6 + x) : (15
+ x) :: (20 + x) (43 + x)
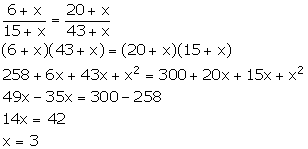
Thus, the required number which should be added is 3.
Solution 7(i)
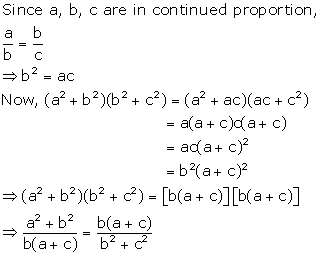
Solution 7(ii)
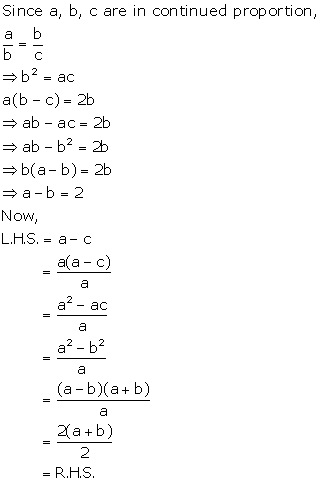
Solution 7(iii)
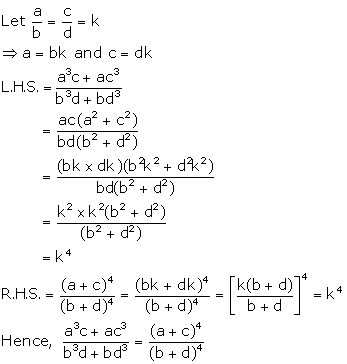
Solution 8
Let the number subtracted be x.
![]() (7 - x) : (17
- x) :: (17 - x) (47 - x)
(7 - x) : (17
- x) :: (17 - x) (47 - x)
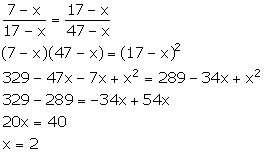
Thus, the required number which should be subtracted is 2.
Solution 9
Since y is the mean proportion between x and z
Therefore, y2 = xz
Now, we have to prove that xy+yz is the mean proportional between x2+y2 and y2+z2, i.e.,
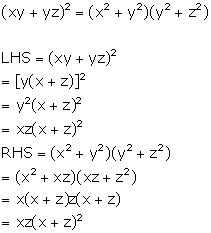
LHS = RHS
Hence, proved.
Solution 10
Given, q is the mean proportional between p and r.
![]() q2 =
pr
q2 =
pr
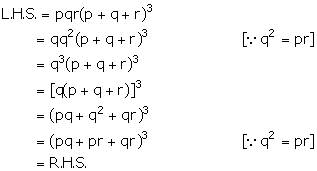
Solution 11
Let x, y and z be the three quantities which are in continued proportion.
Then, x : y :: y : z ![]() y2 = xz ....(1)
y2 = xz ....(1)
Now, we have to prove that
x : z = x2 : y2
That is we need to prove that
xy2 = x2z
LHS = xy2 = x(xz) = x2z = RHS [Using (1)]
Hence, proved.
Solution 12
Given, y is the mean proportional between x and z.
![]() y2 = xz
y2 = xz

Solution 13
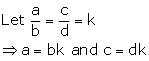
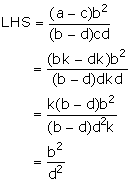
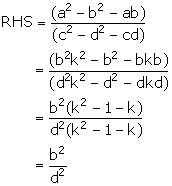
![]() LHS = RHS
LHS = RHS
Hence proved.
Solution 14
Let a and b be the two numbers, whose mean proportional is 12.
![]()
Now, third proportional is 96
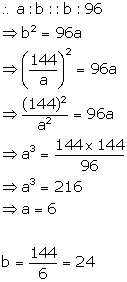
Therefore, the numbers are 6 and 24.
Solution 15
Let the required third proportional be p.
![]()
![]() , p are in
continued proportion.
, p are in
continued proportion.

Solution 16
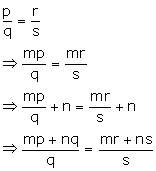
Hence, mp + nq : q = mr + ns : s.
Solution 17

Hence, proved.
Ratio and Proportion (Including Properties and Uses) Exercise Ex. 7(C)
Solution 1

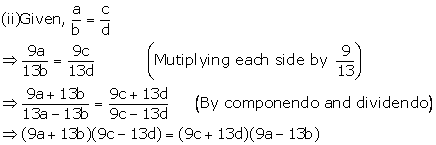

Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4

Solution 5
Given,
![]()
Applying componendo and dividendo,
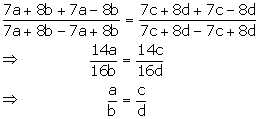
Hence, a: b = c: d.
Solution 6
(i)
x = ![]()

(ii)
![]()
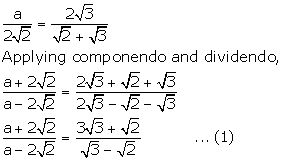

Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9
Given,
![]()
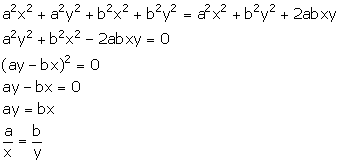
Solution 10
Given, a, b and c are in continued proportion.
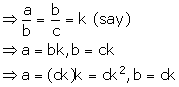
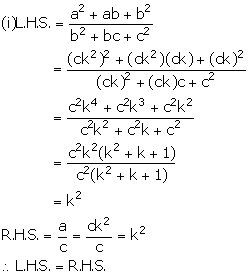
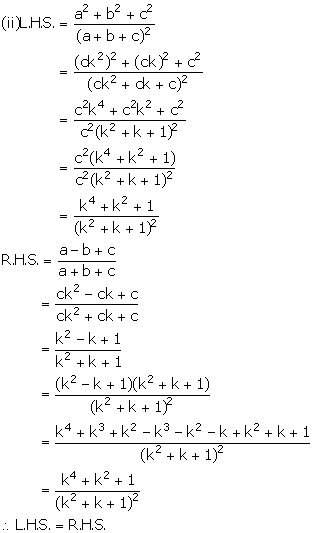
Solution 11


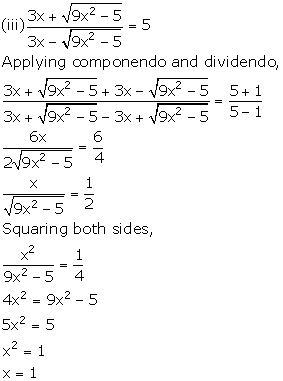
Solution 12
Since, ![]()
Applying componendo and dividendo, we get,
![]()
![]()
Squaring both sides,
![]()
Again applying componendo and dividendo,
![]()
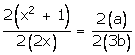
![]()
3bx2 + 3b = 2ax
3bx2 - 2ax + 3b = 0.
Solution 13

Solution 14
![]()
Applying componendo and dividendo,
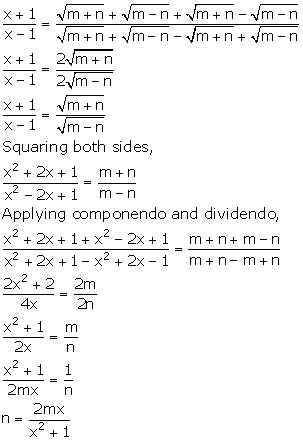
Solution 15
![]()
Applying componendo and dividendo,

Ratio and Proportion (Including Properties and Uses) Exercise Ex. 7(D)
Solution 1
Given,
![]()
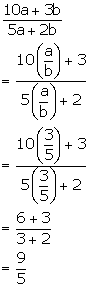
Solution 2
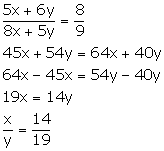
Solution 3
(3x - 4y): (2x - 3y) = (5x - 6y): (4x - 5y)
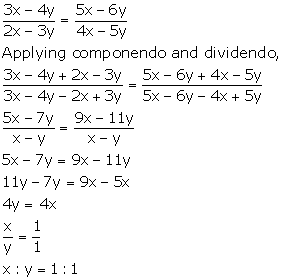
Solution 4
(i)
Duplicate ratio of ![]()
(ii) Triplicate ratio of 2a: 3b = (2a)3: (3b)3 = 8a3 : 27b3
(iii)
Sub-duplicate ratio of 9x2a4 : 25y6b2
= ![]()
(iv)
Sub-triplicate ratio of 216: 343 = ![]()
(v) Reciprocal ratio of 3: 5 = 5: 3
(vi) Duplicate ratio of 5: 6 = 25: 36
Reciprocal ratio of 25: 42 = 42: 25
Sub-duplicate ratio of 36: 49 = 6: 7
Required
compound ratio = ![]()
Solution 5
(i)
(2x + 3): (5x - 38) is the duplicate ratio of ![]()
Duplicate
ratio of ![]()
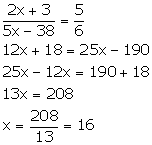
(ii) (2x + 1): (3x + 13) is the sub-duplicate ratio of 9: 25
Sub-duplicate ratio of 9: 25 = 3: 5
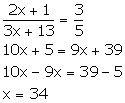
(iii) (3x - 7): (4x + 3) is the sub-triplicate ratio of 8: 27
Sub-triplicate ratio of 8: 27 = 2: 3
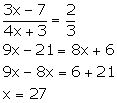
Solution 6
Let the required quantity which is to be added be p.
Then, we have:
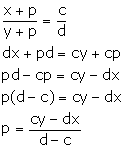
Solution 7

Solution 8
15(2x2 - y2) = 7xy
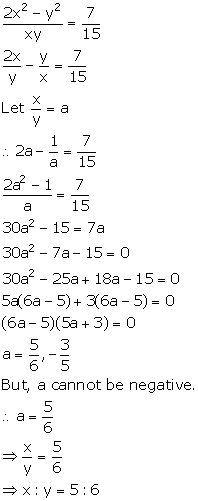
Solution 9
(i) Let the fourth proportional to 2xy, x2 and y2 be n.
![]() 2xy: x2 = y2: n
2xy: x2 = y2: n
![]() 2xy
2xy ![]() n = x2
n = x2![]() y2
y2
![]() n =
n =![]()
(ii) Let the third proportional to a2 - b2 and a + b be n.
![]() a2 - b2, a + b and n are in continued proportion.
a2 - b2, a + b and n are in continued proportion.
![]() a2 - b2 : a + b = a + b : n
a2 - b2 : a + b = a + b : n
![]() n =
n =![]()
(iii) Let the mean proportion to (x - y) and (x3 - x2y) be n.
![]() (x - y), n, (x3 - x2y) are in continued proportion
(x - y), n, (x3 - x2y) are in continued proportion
![]() (x - y) : n = n : (x3 - x2y)
(x - y) : n = n : (x3 - x2y)
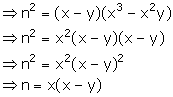
Solution 10
Let the required numbers be a and b.
Given, 14 is the mean proportional between a and b.
![]() a: 14 = 14: b
a: 14 = 14: b
![]() ab = 196
ab = 196
![]()
Also, given, third proportional to a and b is 112.
![]() a: b = b: 112
a: b = b: 112
![]()
Using (1), we have:
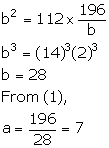
Thus, the two numbers are 7 and 28.
Solution 11
Given,
![]()
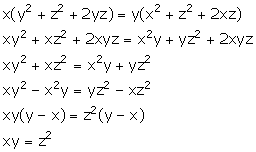
Hence, z is mean proportional between x and y.
Solution 12

Solution 13
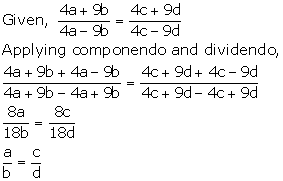
Solution 14
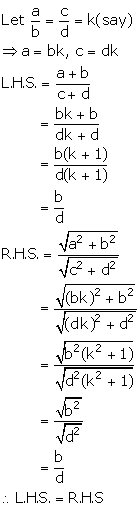
Solution 15
Ratio of number of boys to the number of girls = 3: 1
Let the number of boys be 3x and number of girls be x.
![]() 3x + x = 36
3x + x = 36
4x = 36
x = 9
![]() Number of boys
= 27
Number of boys
= 27
Number of girls = 9
Le n number of girls be added to the council.
From given information, we have:
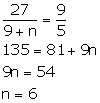
Thus, 6 girls are added to the council.
Solution 16
7x - 15y = 4x + y
7x - 4x = y + 15y
3x = 16y
![]()

Solution 17
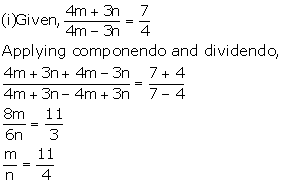

Solution 18
![]() x, y, z are in continued proportion,
x, y, z are in continued proportion,
![]()
![]()
Therefore,
![]()
![]()
![]() (By alternendo)
(By alternendo)
![]()
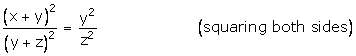
![]()

![]()
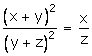
Hence Proved.
Solution 19
x = 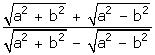
By componendo and dividendo,
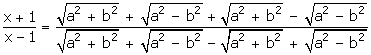
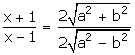
Squaring both sides,
![]()
By componendo and dividendo,
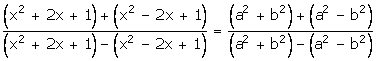
![]()
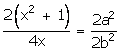
![]()
![]()
![]() b2 =
b2 =
![]()
Hence Proved.
Solution 20

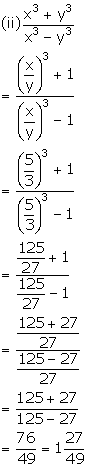
Solution 21

Solution 22

Solution 23

Solution 24
![]()

Solution 25
Given that b is the mean proportion between a and c.
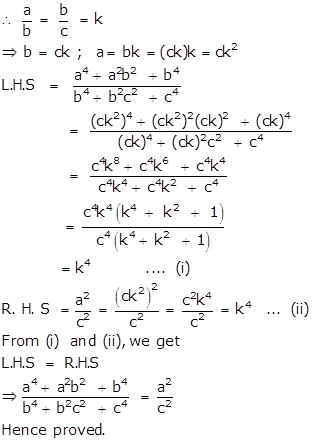
Solution 26
i.
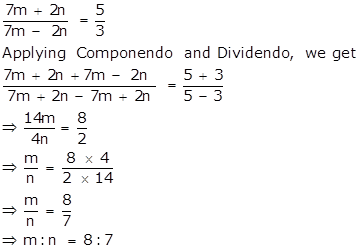
ii.
From (i),
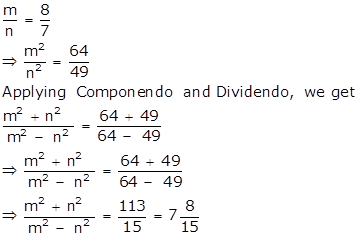
Solution 27
i. (2x2 - 5y2): xy = 1: 3
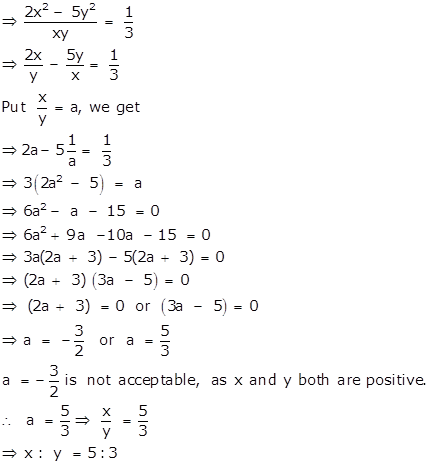
ii.