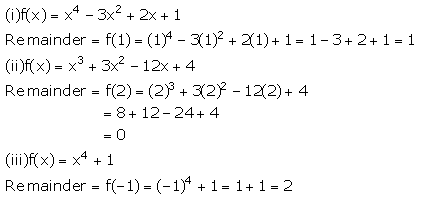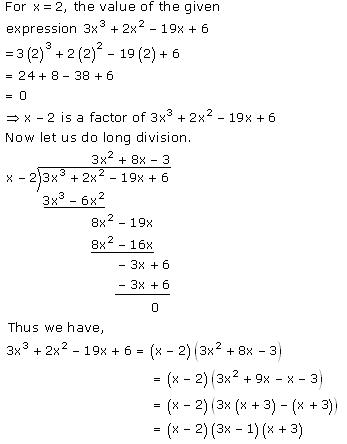Class 10 SELINA Solutions Maths Chapter 8 - Remainder And Factor Theorems
Remainder And Factor Theorems Exercise Ex. 8(A)
Solution 1
By remainder theorem we know that when a polynomial f (x) is divided by x - a, then the remainder is f(a).
Solution 2
(x - a) is a factor of a polynomial f(x) if the remainder, when f(x) is divided by (x - a), is 0, i.e., if f(a) = 0.
Solution 3
By remainder theorem we know that when a polynomial f (x) is divided by x - a, then the remainder is f(a).
Let f(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 - 5x - 6
(i) f (-1) = 2(-1)3 + 3(-1)2 - 5(-1) - 6 = -2 + 3 + 5 - 6 = 0
Thus, (x + 1) is a factor of the polynomial f(x).
(ii)
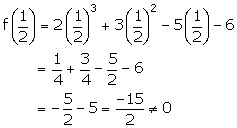
Thus, (2x - 1) is not a factor of the polynomial f(x).
(iii) f (-2) = 2(-2)3 + 3(-2)2 - 5(-2) - 6 = -16 + 12 + 10 - 6 = 0
Thus, (x + 2) is a factor of the polynomial f(x).
Solution 4
(i) 2x + 1 is a factor of f(x) = 2x2 + ax - 3.
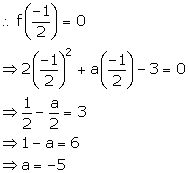
(ii) 3x - 4 is a factor of g(x) = 3x2 + 2x - k.
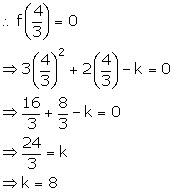
Solution 5
Let f(x) = x3 + ax2 + bx - 12
x - 2 = 0 ![]() x = 2
x = 2
x - 2 is a factor of f(x). So, remainder = 0
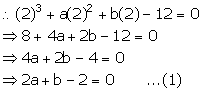
x + 3 = 0 ![]() x = -3
x = -3
x + 3 is a factor of f(x). So, remainder = 0
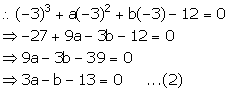
Adding (1) and (2), we get,
5a - 15 = 0
![]() a = 3
a = 3
Putting the value of a in (1), we get,
6 + b - 2 = 0
![]() b = -4
b = -4
Solution 6
Let f(x) = (3k + 2)x3 + (k - 1)
2x + 1 = 0 ![]()
![]()
Since, 2x + 1 is a factor of f(x), remainder is 0.
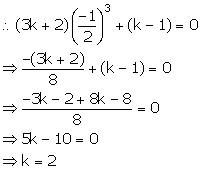
Solution 7
f(x) = 2x5 - 6x4 - 2ax3 + 6ax2 + 4ax + 8
x - 2 = 0 ![]() x = 2
x = 2
Since, x - 2 is a factor of f(x), remainder = 0.
2(2)5 - 6(2)4 - 2a(2)3 + 6a(2)2 + 4a(2) + 8 = 0
64 - 96 - 16a + 24a + 8a + 8 = 0
-24 + 16a = 0
16a = 24
a = 1.5
Solution 8
Let f(x) = x3 + (3m + 1) x2 + nx - 18
x - 1 = 0 ![]() x = 1
x = 1
x - 1 is a factor of f(x). So, remainder = 0
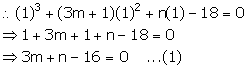
x + 2 = 0 ![]() x = -2
x = -2
x + 2 is a factor of f(x). So, remainder = 0
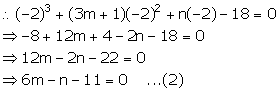
Adding (1) and (2), we get,
9m - 27 = 0
m = 3
Putting the value of m in (1), we get,
3(3) + n - 16 =0
9 + n - 16 = 0
n = 7
Solution 9
Let f(x) = x3 + 2x2 - kx + 4
x - 2 = 0 ![]() x = 2
x = 2
On dividing f(x) by x - 2, it leaves a remainder k.
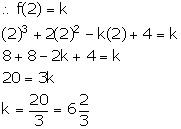
Solution 10
Let f(x) = ax3 + 9x2 + 4x - 10
x + 3 = 0 ![]() x = -3
x = -3
On dividing f(x) by x + 3, it leaves a remainder 5.
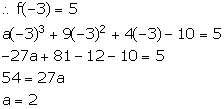
Solution 11
Let f(x) = x3 + ax2 + bx + 6
x - 2 = 0 ![]() x = 2
x = 2
Since, x - 2 is a factor, remainder = 0
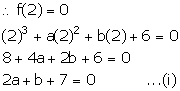
x - 3 = 0 ![]() x = 3
x = 3
On dividing f(x) by x - 3, it leaves a remainder 3.
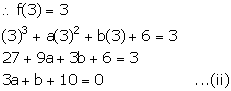
Subtracting (i) from (ii), we get,
a + 3 = 0
a = -3
Substituting the value of a in (i), we get,
-6 + b + 7 = 0
b = -1
Solution 12
Let f(x) = 2x3 + ax2 + bx - 2
2x - 3 = 0 ![]() x =
x = ![]()
On dividing f(x) by 2x - 3, it leaves a remainder 7.

x + 2 = 0 ![]() x = -2
x = -2
On dividing f(x) by x + 2, it leaves a remainder 0.
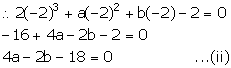
Adding (i) and (ii), we get,
7a - 21 = 0
a = 3
Substituting the value of a in (i), we get,
![]()
9 + 2b - 3 = 0
2b = -6
b = -3
Solution 13
Let the number k be added and the resulting polynomial be f(x).
So, f(x) = 3x3 - 5x2 + 6x + k
It is given that when f(x) is divided by (x - 3), the remainder is 8.
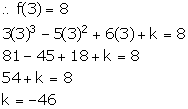
Thus, the required number is -46.
Solution 14
Let the number to be subtracted be k and the resulting polynomial be f(x).
So, f(x) = x3 + 3x2 - 8x + 14 - k
It is given that when f(x) is divided by (x - 2), the remainder is 10.
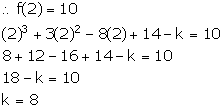
Thus, the required number is 8.
Solution 15
Let f(x) = 2x3 - 7x2 + ax - 6
x - 2 = 0 ![]() x = 2
x = 2
When f(x) is divided by (x - 2), remainder = f(2)
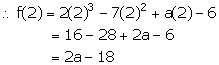
Let g(x) = x3 - 8x2 + (2a + 1)x - 16
When g(x) is divided by (x - 2), remainder = g(2)
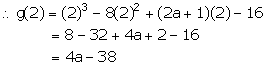
By the given condition, we have:
f(2) = g(2)
2a - 18 = 4a - 38
4a - 2a = 38 - 18
2a = 20
a = 10
Thus, the value of a is 10.
Solution 16
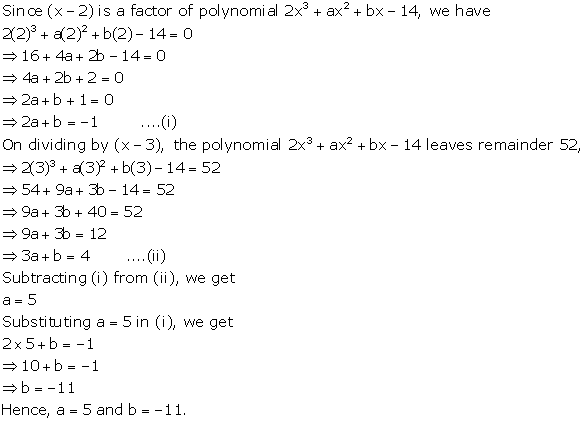
Solution 17
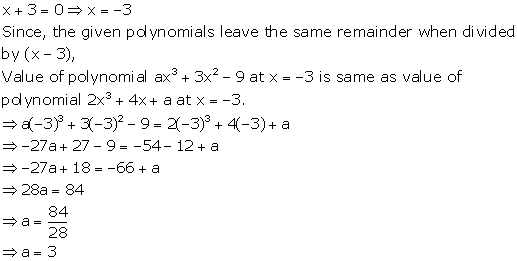
Remainder And Factor Theorems Exercise Ex. 8(B)
Solution 1
(i) Let f(x) = x3 - 2x2 - 9x + 18
x - 2 = 0 ![]() x = 2
x = 2
![]() Remainder = f(2)
Remainder = f(2)
= (2)3 - 2(2)2 - 9(2) + 18
= 8 - 8 - 18 + 18
= 0
Hence, (x - 2) is a factor of f(x).
Now, we have:
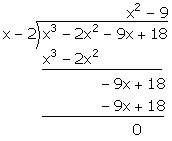
![]() x3 - 2x2 - 9x + 18 = (x - 2) (x2 - 9) = (x - 2) (x + 3) (x - 3)
x3 - 2x2 - 9x + 18 = (x - 2) (x2 - 9) = (x - 2) (x + 3) (x - 3)
(ii) Let f(x) = 2x3 + 5x2 - 28x - 15
x + 5 = 0 ![]() x = -5
x = -5
![]() Remainder = f(-5)
Remainder = f(-5)
= 2(-5)3 + 5(-5)2 - 28(-5) - 15
= -250 + 125 + 140 - 15
= -265 + 265
= 0
Hence, (x + 5) is a factor of f(x).
Now, we have:
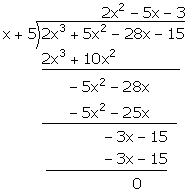
![]() 2x3 + 5x2 - 28x - 15 = (x + 5) (2x2 - 5x - 3)
2x3 + 5x2 - 28x - 15 = (x + 5) (2x2 - 5x - 3)
= (x + 5) [2x2 - 6x + x - 3]
= (x + 5) [2x(x - 3) + 1(x - 3)]
= (x + 5) (2x + 1) (x - 3)
(iii) Let f(x) = 3x3 + 2x2 - 3x - 2
3x + 2 = 0 ![]()

Hence, (3x + 2) is a factor of f(x).
Now, we have:
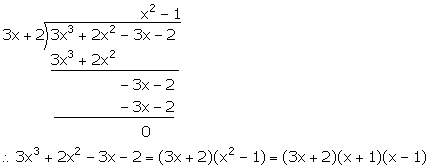
Solution 2
(i)
(ii) Let f(x) = 2x3 + x2 - 13x + 6
For x = 2,
f(x) = f(2) = 2(2)3 + (2)2 - 13(2) + 6 = 16 + 4 - 26 + 6 = 0
Hence, (x - 2) is a factor of f(x).
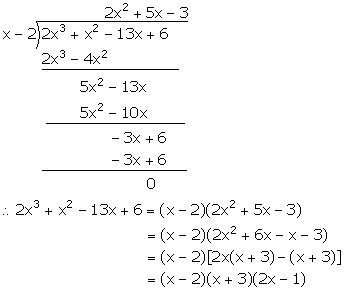
(iii) f(x) = 3x3 + 2x2 - 23x - 30
For x = -2,
f(x) = f(-2) = 3(-2)3 + 2(-2)2 - 23(-2) - 30
= -24 + 8 + 46 - 30 = -54 + 54 = 0
Hence, (x + 2) is a factor of f(x).
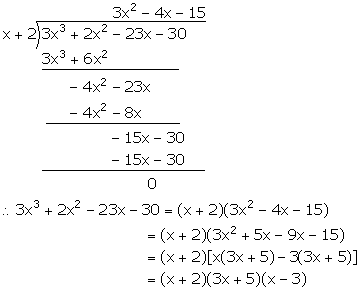
(iv) f(x) = 4x3 + 7x2 - 36x - 63
For x = 3,
f(x) = f(3) = 4(3)3 + 7(3)2 - 36(3) - 63
= 108 + 63 - 108 - 63 = 0
Hence, (x + 3) is a factor of f(x).
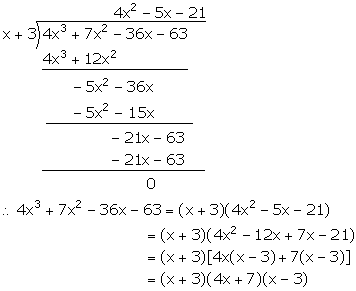
(v) f(x) = x3 + x2 - 4x - 4
For x = -1,
f(x) = f(-1) = (-1)3 + (-1)2 - 4(-1) - 4
= -1 + 1 + 4 - 4 = 0
Hence, (x + 1) is a factor of f(x).
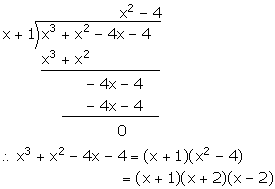
Solution 3
Let f(x) = 3x3 + 10x2 + x - 6
For x = -1,
f(x) = f(-1) = 3(-1)3 + 10(-1)2 + (-1) - 6 = -3 + 10 - 1 - 6 = 0
Hence, (x + 1) is a factor of f(x).
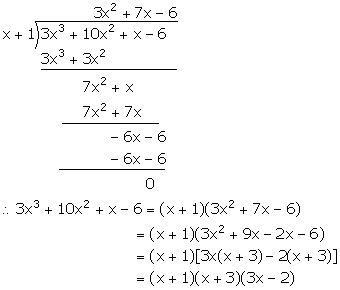
Now, 3x3 + 10x2 + x - 6 = 0
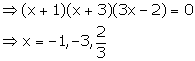
Solution 4
f (x) = 2x3 - 7x2 - 3x + 18
For x = 2,
f(x) = f(2) = 2(2)3 - 7(2)2 - 3(2) + 18
= 16 - 28 - 6 + 18 = 0
Hence, (x - 2) is a factor of f(x).
Solution 5
f(x) = x3 + 3x2 + ax + b
Since, (x - 2) is a factor of f(x), f(2) = 0
![]() (2)3 + 3(2)2 + a(2) + b = 0
(2)3 + 3(2)2 + a(2) + b = 0
![]() 8 + 12 + 2a + b = 0
8 + 12 + 2a + b = 0
![]() 2a + b + 20 = 0 ...(i)
2a + b + 20 = 0 ...(i)
Since, (x + 1) is a factor of f(x), f(-1) = 0
![]() (-1)3 + 3(-1)2 + a(-1) + b = 0
(-1)3 + 3(-1)2 + a(-1) + b = 0
![]() -1 + 3 - a + b = 0
-1 + 3 - a + b = 0
![]() -a + b + 2 = 0 ...(ii)
-a + b + 2 = 0 ...(ii)
Subtracting (ii) from (i), we get,
3a + 18 = 0
![]() a = -6
a = -6
Substituting the value of a in (ii), we get,
b = a - 2 = -6 - 2 = -8
![]() f(x) = x3 + 3x2 - 6x - 8
f(x) = x3 + 3x2 - 6x - 8
Now, for x = -1,
f(x) = f(-1) = (-1)3 + 3(-1)2 - 6(-1) - 8 = -1 + 3 + 6 - 8 = 0
Hence, (x + 1) is a factor of f(x).
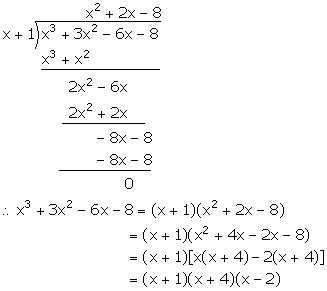
Solution 6
Let f(x) = 4x3 - bx2 + x - c
It is given that when f(x) is divided by (x + 1), the remainder is 0.
![]() f(-1) = 0
f(-1) = 0
4(-1)3 - b(-1)2 + (-1) - c = 0
-4 - b - 1 - c = 0
b + c + 5 = 0 ...(i)
It is given that when f(x) is divided by (2x - 3), the remainder is 30.
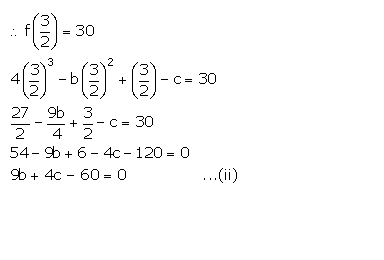
Multiplying (i) by 4 and subtracting it from (ii), we get,
5b + 40 = 0
b = -8
Substituting the value of b in (i), we get,
c = -5 + 8 = 3
Therefore, f(x) = 4x3 + 8x2 + x - 3
Now, for x = -1, we get,
f(x) = f(-1) = 4(-1)3 + 8(-1)2 + (-1) - 3 = -4 + 8 - 1 - 3 = 0
Hence, (x + 1) is a factor of f(x).
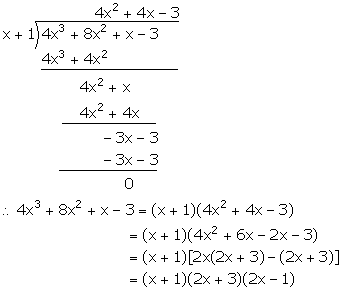
Solution 7
f(x) = x2 + px + q
It is given that (x + a) is a factor of f(x).
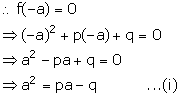
g(x) = x2 + mx + n
It is given that (x + a) is a factor of g(x).
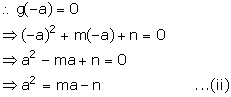
From (i) and (ii), we get,
pa - q = ma - n
n - q = a(m - p)
![]()
Hence, proved.
Solution 8
Let f(x) = ax3 + 3x2 - 3
When f(x) is divided by (x - 4), remainder = f(4)
f(4) = a(4)3 + 3(4)2 - 3 = 64a + 45
Let g(x) = 2x3 - 5x + a
When g(x) is divided by (x - 4), remainder = g(4)
g(4) = 2(4)3 - 5(4) + a = a + 108
It is given that f(4) = g(4)
64a + 45 = a + 108
63a = 63
a = 1
Solution 9
Let f(x) = x3 - ax2 + x + 2
It is given that (x - a) is a factor of f(x).
![]() Remainder =
f(a) = 0
Remainder =
f(a) = 0
a3 - a3 + a + 2 = 0
a + 2 = 0
a = -2
Solution 10
Let the number to be subtracted from the given polynomial be k.
Let f(y) = 3y3 + y2 - 22y + 15 - k
It is given that f(y) is divisible by (y + 3).
![]() Remainder =
f(-3) = 0
Remainder =
f(-3) = 0
3(-3)3 + (-3)2 - 22(-3) + 15 - k = 0
-81 + 9 + 66 + 15 - k = 0
9 - k = 0
k = 9
Remainder And Factor Theorems Exercise Ex. 8(C)
Solution 1
Let f(x) = x3 - 7x2 + 14x - 8
f(1) = (1)3 - 7(1)2 + 14(1) - 8 = 1 - 7 + 14 - 8 = 0
Hence, (x - 1) is a factor of f(x).
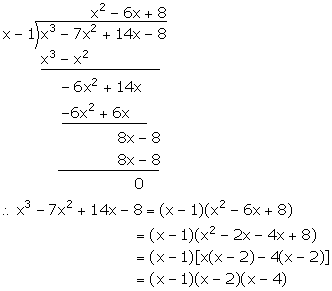
Solution 2

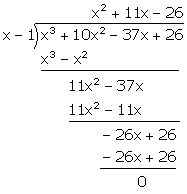
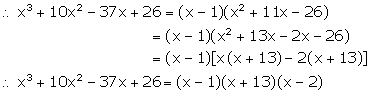
Solution 3
Let f(x) = x3 + 3x2 - mx + 4
According to the given information,
f(2) = m + 3
(2)3 + 3(2)2 - m(2) + 4 = m + 3
8 + 12 - 2m + 4 = m + 3
24 - 3 = m + 2m
3m = 21
m = 7
Solution 4
Let the required number be k.
Let f(x) = 3x3 - 8x2 + 4x - 3 - k
According to the given information,
f (-2) = 0
3(-2)3 - 8(-2)2 + 4(-2) - 3 - k = 0
-24 - 32 - 8 - 3 - k = 0
-67 - k = 0
k = -67
Thus, the required number is -67.
Solution 5
Let f(x) = x3 + (a + 1)x2 - (b - 2)x - 6
Since, (x + 1) is a factor of f(x).
![]() Remainder = f(-1) = 0
Remainder = f(-1) = 0
(-1)3 + (a + 1)(-1)2 - (b - 2) (-1) - 6 = 0
-1 + (a + 1) + (b - 2) - 6 = 0
a + b - 8 = 0 ...(i)
Since, (x - 2) is a factor of f(x).
![]() Remainder = f(2) = 0
Remainder = f(2) = 0
(2)3 + (a + 1) (2)2 - (b - 2) (2) - 6 = 0
8 + 4a + 4 - 2b + 4 - 6 = 0
4a - 2b + 10 = 0
2a - b + 5 = 0 ...(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we get,
3a - 3 = 0
a = 1
Substituting the value of a in (i), we get,
1 + b - 8 = 0
b = 7
![]() f(x) = x3 + 2x2 - 5x - 6
f(x) = x3 + 2x2 - 5x - 6
Now, (x + 1) and (x - 2) are factors of f(x). Hence, (x + 1) (x - 2) = x2 - x - 2 is a factor of f(x).
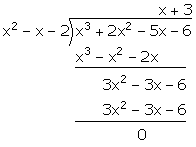
![]() f(x) = x3 + 2x2 - 5x - 6 = (x + 1) (x - 2) (x + 3)
f(x) = x3 + 2x2 - 5x - 6 = (x + 1) (x - 2) (x + 3)
Solution 6
Let f(x) = x2 + ax + b
Since, (x - 2) is a factor of f(x).
![]() Remainder = f(2) = 0
Remainder = f(2) = 0
(2)2 + a(2) + b = 0
4 + 2a + b = 0
2a + b = -4 ...(i)
It is given that:
a + b = 1 ...(ii)
Subtracting (ii) from (i), we get,
a = -5
Substituting the value of a in (ii), we get,
b = 1 - (-5) = 6
Solution 7
Let f(x) = x3 + 6x2 + 11x + 6
For x = -1
f(-1) = (-1)3 + 6(-1)2 + 11(-1) + 6
= -1 + 6 - 11 + 6 = 12 - 12 = 0
Hence, (x + 1) is a factor of f(x).
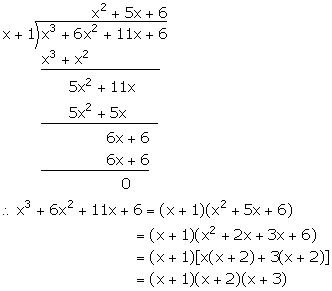
Solution 8
Let f(x) = mx3 + 2x2 - 3
g(x) = x2 - mx + 4
It is given that f(x) and g(x) leave the same remainder when divided by (x - 2). Therefore, we have:
f (2) = g (2)
m(2)3 + 2(2)2 - 3 = (2)2 - m(2) + 4
8m + 8 - 3 = 4 - 2m + 4
10m = 3
m
= ![]()
Solution 9
Let f(x) = px3 + 4x2 - 3x + q
It is given that f(x) is completely divisible by (x2 - 1) = (x + 1)(x - 1).
Therefore, f(1) = 0 and f(-1) = 0
f(1) = p(1)3 + 4(1)2 - 3(1) + q = 0
p + q + 1 = 0 ...(i)
f(-1) = p(-1)3 + 4(-1)2 - 3(-1) + q = 0
-p + q + 7 = 0 ...(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we get,
2q + 8 = 0
q = -4
Substituting the value of q in (i), we get,
p = -q - 1 = 4 - 1 = 3
![]() f(x) = 3x3 + 4x2 - 3x - 4
f(x) = 3x3 + 4x2 - 3x - 4
Given that f(x) is completely divisible by (x2 - 1).
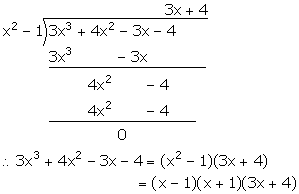
Solution 10
Let the required number be k.
Let f(x) = x2 + x + 3 + k
It is given that f(x) is divisible by (x + 3).
![]() Remainder = 0
Remainder = 0
f (-3) = 0
(-3)2 + (-3) + 3 + k = 0
9 - 3 + 3 + k = 0
9 + k = 0
k = -9
Thus, the required number is -9.
Solution 11
It is given that when the polynomial x3 + 2x2 - 5ax - 7 is divided by (x - 1), the remainder is A.
![]() (1)3 + 2(1)2 - 5a(1) - 7 = A
(1)3 + 2(1)2 - 5a(1) - 7 = A
1 + 2 - 5a - 7 = A
- 5a - 4 = A ...(i)
It is also given that when the polynomial x3 + ax2 - 12x + 16 is divided by (x + 2), the remainder is B.
![]() x3 + ax2 - 12x + 16 = B
x3 + ax2 - 12x + 16 = B
(-2)3 + a(-2)2 - 12(-2) + 16 = B
-8 + 4a + 24 + 16 = B
4a + 32 = B ...(ii)
It is also given that 2A + B = 0
Using (i) and (ii), we get,
2(-5a - 4) + 4a + 32 = 0
-10a - 8 + 4a + 32 = 0
-6a + 24 = 0
6a = 24
a = 4
Solution 12
Let f(x) = (a - 1)x3 + (a + 1)x2 - (2a + 1)x - 15
It is given that (3x + 5) is a factor of f(x).
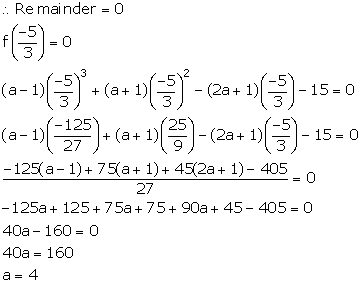
![]() f(x) = (a - 1)x3 + (a + 1)x2 - (2a + 1)x - 15
f(x) = (a - 1)x3 + (a + 1)x2 - (2a + 1)x - 15
= 3x3 + 5x2 - 9x - 15
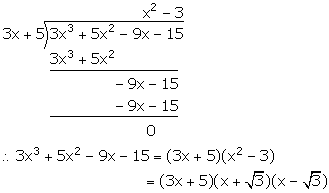
Solution 13
If (x - 3) divides f(x) = x3 - px2 + x + 6, then,
Remainder = f(3) = 33 - p(3)2 + 3 + 6 = 36 - 9p
If (x - 3) divides g(x) = 2x3 - x2 - (p + 3) x - 6, then
Remainder = g(3) = 2(3)3 - (3)2 - (p + 3) (3) - 6 = 30 - 3p
Now, f(3) = g(3)
![]() 36 - 9p = 30 -
3p
36 - 9p = 30 -
3p
![]() -6p = -6
-6p = -6
![]() p = 1
p = 1
Solution 14
f(x) = 2x3 + x2 - 13x + 6
Factors of constant term 6 are ![]() 1,
1, ![]() 2,
2, ![]() 3,
3, ![]() 6.
6.
Putting x = 2, we have:
f(2) = 2(2)3 + 22 - 13 (2) + 6 = 16 + 4 - 26 + 6 = 0
Hence (x - 2) is a factor of f(x).

Solution 15
Let f(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 - kx + 5
Using Remainder Theorem, we have
f(2) = 7
∴ 2(2)3 + 3(2)2 - k(2) + 5 = 7
∴ 16 + 12 - 2k + 5 = 7
∴ 33 - 2k = 7
∴ 2k = 26
∴ k = 13
Solution 16
Here, f(x) = 16x3 - 8x2 + 4x + 7
Let the number subtracted be k from the given polynomial f(x).
Given that 2x + 1 is a factor of f(x).
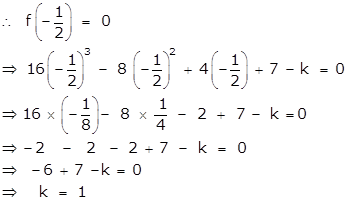
Therefore 1 must be subtracted from 16x3 - 8x2 + 4x + 7 so that the resulting expression has 2x + 1 as a factor.