Class 10 SELINA Solutions Maths Chapter 6 - Solving (simple) Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations)
Selina Solutions is the must-have comprehensive guide that aidsICSE Class 10 Math students who are searching for reliable study resources.
In ICSE Class 10, mathematics is a very important academic milestone that lays the footing for further advancements of mathematical concepts for higher studies. The subject encompasses a wide spectrum of topics, including trigonometry, algebra, geometry, mensuration, etc. So, students who aspire to perform well must practise every chapter thoroughly to get clarity on the basic concepts.
Quadratic Equations is one such important chapter in ICSE Class 10 Math which requires consistent practice. Selina solutions serve as a quick fix for students who wish to get through the concepts and achieve good marks. This reliable reference material delivers easy step-by-step explanations for all exercises of the chapter in the book.
Importance of Selina Solutions for Chapter- Quadratic Equations
The following points will help understand why Selina Solutions for quadratic equations are crucial for students:
- Complete Course Coverage: All the topics specified by the ICSE Board for quadratic equations are covered in the solution book. Every question of each exercise is solved in a descriptive but to-the-point manner for a holistic learning experience.
- Accuracy and Clarity: Selina Solutions offers carefully given solutions that are apt for providing accurate and clear descriptions. Having clarity in understanding the underlying principles and formulas of quadratic equations is crucial for students to build a strong mathematical foundation.
- Devoted Practice: Students get access to a reliable resource that they can refer to if they get stuck on any question. Thus these solutions give a motivation for practice that results in much-sweetened confidence and strong problem-solving skills.
- Exam Cautiousness: An ICSE Math student of Class 10 can refer to Selina Solutions for last-minute clarification and revisions. It serves as a rich source for quick revisions of the key quadratic equation formulas and concepts owing to its organised approach.
To prepare thoroughly and receive the highest possible grade in maths on their final exams, students can also refer to sample papers and put what they have learned into implementation. They can also viewvideos on key concepts, rehearseMCQ problems, and browse throughadditional study materials. Let us beat the challenges of mathematics through a comprehensive and practice-oriented approach and undertake an expedition towards mathematical excellence!
Solving (simple) Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Exercise Ex. 6(A)
Solution 1
Let the two consecutive integers be x and x + 1.
From the given information,
x(x + 1) = 56
x2 + x - 56 = 0
(x + 8) (x - 7) = 0
x = -8 or 7
Thus, the required integers are - 8 and -7; 7 and 8.
Solution 2
Let the numbers be x and x + 1.
From the given information,
x2 + (x + 1)2 = 41
2x2 + 2x + 1 - 41 = 0
x2 + x - 20 = 0
(x + 5) (x - 4) = 0
x = -5, 4
But, -5 is not a natural number. So, x = 4.
Thus, the numbers are 4 and 5.
Solution 3
Let the two numbers be x and x + 5.
From the given information,
x2 + (x + 5)2 = 97
2x2 + 10x + 25 - 97 = 0
2x2 + 10x - 72 = 0
x2 + 5x - 36 = 0
(x + 9) (x - 4) = 0
x = -9 or 4
Since, -9 is not a natural number. So, x = 4.
Thus, the numbers are 4 and 9.
Solution 4
Let the numbers be x and ![]()
From the given information,
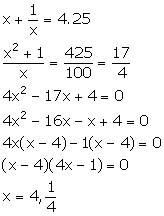
x = 4 ![]()
x = ![]()
![]() x = 4
x = 4
Thus, the numbers are 4 and ![]()
Solution 5
Let the numbers be x and x + 3.
From the given information,
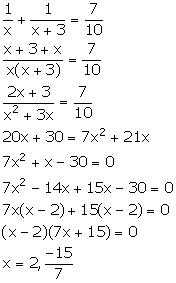
Since, x is a natural number, so x = 2.
Thus, the numbers are 2 and 5.
Solution 6
Let the two parts be x and x - 15.
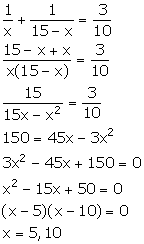
x = 5 ![]() One part = 5 and other part = 10
One part = 5 and other part = 10
x = 10 ![]() One part = 10 and other part = 5
One part = 10 and other part = 5
Thus, the required two parts are 5 and 10.
Solution 7
Let the two numbers be x and y, y being the bigger number. From the given information,
x2 + y2 = 208 ..... (i)
y2 = 18x ..... (ii)
From (i), we get y2=208 - x2. Putting this in (ii), we get,
208 - x2 = 18x
![]() x2 + 18x - 208 = 0
x2 + 18x - 208 = 0
![]() x2 + 26X - 8X - 208 = 0
x2 + 26X - 8X - 208 = 0
![]() x(x + 26) - 8(x + 26) = 0
x(x + 26) - 8(x + 26) = 0
![]() (x - 8)(x + 26) = 0
(x - 8)(x + 26) = 0
![]() x can't be a negative number , hence x = 8
x can't be a negative number , hence x = 8
![]() Putting x = 8 in (ii), we get y2 = 18 x 8=144
Putting x = 8 in (ii), we get y2 = 18 x 8=144
![]() y = 12, since y is a positive integer
y = 12, since y is a positive integer
Hence, the two numbers are 8 and 12.
Solution 8
Let the consecutive positive even numbers be x and x + 2.
From the given information,
x2 + (x + 2)2 = 52
2x2 + 4x + 4 = 52
2x2 + 4x - 48 = 0
x2 + 2x - 24 = 0
(x + 6) (x - 4) = 0
x = -6, 4
Since, the numbers are positive, so x = 4.
Thus, the numbers are 4 and 6.
Solution 9
Let the consecutive positive odd numbers be x and x + 2.
From the given information,
x2 + (x + 2)2 = 74
2x2 + 4x + 4 = 74
2x2 + 4x - 70 = 0
x2 + 2x - 35 = 0
(x + 7)(x - 5) = 0
x = -7, 5
Since, the numbers are positive, so, x = 5.
Thus, the numbers are 5 and 7.
Solution 10
Let the required fraction be![]() .
.
From the given information,
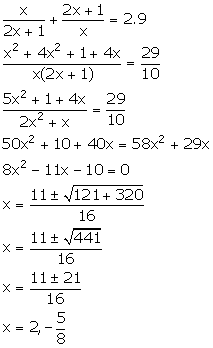
Thus, the required fraction is ![]() .
.
Solution 11
Given, three positive numbers are
in the ratio![]()
Let the numbers be 6x, 4x and 3x.
From the given information,
(6x)2 + (4x)2 + (3x)2 = 244
36x2 + 16x2 + 9x2 = 244
61x2 = 244
x2 = 4
x = ![]()
Since, the numbers are positive, so x = 2.
Thus, the numbers are 12, 8 and 6.
Solution 12
Let the two parts be x and y.
From the given information,
x + y = 20 ![]()
3x2 = (20 - x) + 10
3x2 = 30 - x
3x2 + x - 30 = 0
3x2 - 9x + 10x - 30 = 0
3x(x - 3) + 10(x - 3) = 0
(x - 3) (3x + 10) = 0
x = 3, ![]()
Since, x cannot be equal to![]() , so, x = 3.
, so, x = 3.
Thus, one part is 3 and other part is 20 - 3 = 17.
Solution 13
Let the numbers be x - 1, x and x + 1.
From the given information,
x2 = (x + 1)2 - (x - 1)2 + 60
x2 = x2 + 1 + 2x - x2 - 1 + 2x + 60
x2 = 4x + 60
x2 - 4x - 60 = 0
(x - 10) (x + 6) = 0
x = 10, -6
Since, x is a natural number, so x = 10.
Thus, the three numbers are 9, 10 and 11.
Solution 14
Let the numbers be p - 1, p and p + 1.
From the given information,
3(p + 1)2 = (p - 1)2 + p2 + 67
3p2 + 6p + 3 = p2 + 1 - 2p + p2 + 67
p2 + 8p - 65 = 0
(p + 13)(p - 5) = 0
p = -13, 5
Since, the numbers are positive so p cannot be equal to -13.
Thus, p = 5.
Solution 15
Work done by A in one day = ![]()
Work done by B in one day = ![]()
Together A and B can do the work in 15 days. Therefore, we have:
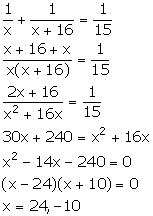
Since, x cannot be negative.
Thus, x = 24.
Solution 16
Let one pipe fill the cistern in x hours and the other fills it in (x - 3) hours.
Given that the two pipes together
can fill the cistern in 6 hours 40 minutes, i.e., ![]()
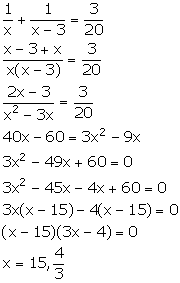
If x =![]() , then x - 3 =
, then x - 3 =![]() , which is not possible.
, which is not possible.
So, x = 15.
Thus, one pipe fill the cistern in 15 hours and the other fills in (x - 3) = 15 - 3 = 12 hours.
Solution 17
Let the smaller part be x.
Then, (larger part)2 = 8x
\
larger part = ![]()
Now, the sum of the squares of both the terms is given to be 208

Thus, the required number is 2 + 4 = 6.
Solving (simple) Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Exercise Ex. 6(B)
Solution 1
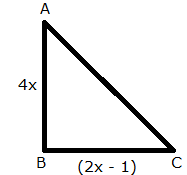
Area of triangle = 30 cm2
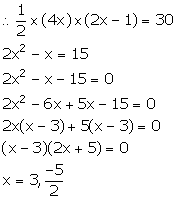
But, x cannot be negative, so x = 3.
Thus, we have:
AB
= 4 ![]() 3 cm = 12 cm
3 cm = 12 cm
BC
= (2 ![]() 3 - 1) cm = 5
cm
3 - 1) cm = 5
cm
CA
= ![]() (Using
Pythagoras theorem)
(Using
Pythagoras theorem)
Solution 2
Hypotenuse = 26 cm
The sum of other two sides is 34 cm.
So, let the other two sides be x cm and (34 - x) cm.
Using Pythagoras theorem,
(26)2 = x2 + (34 - x)2
676 = x2 + x2 + 1156 - 68x
2x2 - 68x + 480 = 0
x2 - 34x + 240 = 0
x2 - 10x - 24x + 240 = 0
x(x - 10) - 24(x - 10) = 0
(x - 10) (x - 24) = 0
x = 10, 24
When x = 10, (34 - x) = 24
When x = 24, (34 - x) = 10
Thus, the lengths the three sides of the right-angled triangle are 10 cm, 24 cm and 26 cm.
Solution 3
Longer side = Hypotenuse = (3x + 1) cm
Lengths of other two sides are (x - 1) cm and 3x cm.
Using Pythagoras theorem,
(3x + 1)2 = (x - 1)2 + (3x)2
9x2 + 1 + 6x = x2 + 1 - 2x + 9x2
x2 - 8x = 0
x(x - 8) = 0
x = 0, 8
But, if x = 0, then one side = 3x = 0, which is not possible.
So, x = 8
Thus, the lengths of the sides of the triangle are (x - 1) cm = 7 cm, 3x cm = 24 cm and (3x + 1) cm = 25 cm.
Area
of the triangle = ![]()
Solution 4
Let the hypotenuse of a triangle be x cm.
From the given information,
Length of one side = (x - 1) cm
Length of other side = (x - 18) cm
Using Pythagoras theorem,
x2 = (x - 1)2 + (x - 18)2
x2 = x2 + 1 - 2x + x2 + 324 - 36x
x2 - 38x + 325 = 0
x2 - 13x - 25x + 325 = 0
x(x - 13) - 25(x - 13) = 0
(x - 13) (x - 25) = 0
x = 13, 25
When x = 13, x - 18 = 13 - 18 = -5, which being negative, is not possible.
So, x = 25
Thus, the lengths of the sides of the triangle are x = 25 cm, (x - 1) = 24 cm and (x - 18) = 7 cm.
Solution 5
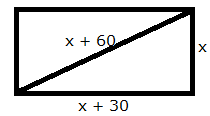
Let the shorter side be x m.
Length of the other side = (x + 30) m
Length of hypotenuse = (x + 60) m
Using Pythagoras theorem,
(x + 60)2 = x2 + (x + 30)2
x2 + 3600 + 120x = x2 + x2 + 900 + 60x
x2 - 60x - 2700 = 0
x2 - 90x + 30x - 2700 = 0
x(x - 90) + 30(x - 90) = 0
(x - 90) (x + 30) = 0
x = 90, -30
But, x cannot be negative. So, x = 90.
Thus, the sides of the rectangle are 90 m and (90 + 30) m = 120 m.
Solution 6
Let the length and the breadth of the rectangle be x m and y m.
Perimeter = 2(x + y) m
![]() 104 = 2(x + y)
104 = 2(x + y)
x + y = 52
y = 52 - x
Area = 640 m2
![]() xy = 640
xy = 640
x(52 - x) = 640
x2 - 52x + 640 = 0
x2 - 32x - 20x + 640 = 0
x(x - 32) - 20 (x - 32) = 0
(x - 32) (x - 20) = 0
x = 32, 20
When x = 32, y = 52 - 32 = 20
When x = 20, y = 52 - 20 = 32
Thus, the length and breadth of the rectangle are 32 m and 20 m.
Solution 7
Let w be the width of the footpath.
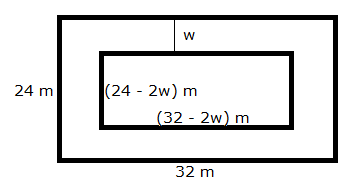
Area of the path = Area of outer rectangle - Area of inner rectangle
![]() 208 = (32)(24)
- (32 - 2w)(24 - 2w)
208 = (32)(24)
- (32 - 2w)(24 - 2w)
208 = 768 - 768 + 64w + 48w - 4w2
4w2 - 112w + 208 = 0
w2 - 28w + 52 = 0
w2 - 26w - 2w + 52 = 0
w(w - 26) - 2(w - 26) = 0
(w - 26) (w - 2) = 0
w = 26, 2
If w = 26, then breadth of inner rectangle = (24 - 52) m = -28 m, which is not possible.
Hence, the width of the footpath is 2 m.
Solution 8
Given that, two squares have sides x cm and (x + 4) cm.
Sum of their area = 656 cm2
![]() x2
+ (x + 4)2 = 656
x2
+ (x + 4)2 = 656
x2 + x2 + 16 + 8x = 656
2x2 + 8x - 640 = 0
x2 + 4x - 320 = 0
x2 + 20x - 16x - 320 = 0
x(x + 20) - 16(x + 20) = 0
(x + 20) (x - 16) = 0
x = -20, 16
But, x being side, cannot be negative.
So, x = 16
Thus, the sides of the two squares are 16 cm and 20 cm.
Solution 9
Let the width of the gravel path be w m.
Length of the rectangular field = 50 m
Breadth of the rectangular field = 40 m
Let the length and breadth of the flower bed be x m and y m respectively.
Therefore, we have:
x + 2w = 50 ... (1)
y + 2w = 40 ... (2)
Also, area of rectangular field = 50 m ![]() 40 m = 2000 m2
40 m = 2000 m2
Area of the flower bed = xy m2
Area of gravel path = Area of rectangular field - Area of flower bed = (2000 - xy) m2
Cost of laying flower bed + Gravel path = Area x cost of laying per sq. m
![]() 52000 = 30
52000 = 30 ![]() xy + 20
xy + 20 ![]() (2000 - xy)
(2000 - xy)
52000 = 10xy + 40000
xy = 1200
Using (1) and (2), we have:
(50 - 2w) (40 - 2w) = 1200
2000 - 180w + 4w2 = 1200
4w2 - 180w + 800 = 0
w2 - 45w + 200 = 0
w2 - 5w - 40w + 200 = 0
w(w - 5) - 40(w - 5) = 0
(w - 5) (w - 40) = 0
w = 5, 40
If w = 40, then x = 50 - 2w = -30, which is not possible.
Thus, the width of the gravel path is 5 m.
Solution 10
Let the size of the larger tiles be x cm.
Area of larger tiles = x2 cm2
Number of larger tiles required to pave an area is 128.
So, the area needed to be paved = 128 x2 cm2 .... (1)
Size of smaller tiles = (x - 2)cm
Area of smaller tiles = (x - 2)2 cm2
Number of larger tiles required to pave an area is 200.
So, the area needed to be paved = 200 (x - 2)2 cm2 .... (2)
Therefore, from (1) and (2), we have:
128 x2 = 200 (x - 2)2
128 x2 = 200x2 + 800 - 800x
72x2 - 800x + 800 = 0
9x2 - 100x + 100 = 0
9x2 - 90x - 10x + 100 = 0
9x(x - 10) - 10(x - 10) = 0
(x - 10)(9x - 10) = 0
x = 10, ![]()
If ![]() , then
, then ![]() , which is not possible.
, which is not possible.
Hence, the size of the larger tiles is 10 cm.
Solution 11
Let the length and breadth of the rectangular sheep pen be x and y respectively.
From the given information,
x + y + x = 70
2x + y = 70 ... (1)
Also, area = xy = 600
Using (1), we have:
x (70 - 2x) = 600
70x - 2x2 = 600
2x2 - 70x + 600 = 0
x2 - 35x + 300 = 0
x2 - 15x - 20x + 300 = 0
x(x - 15) - 20(x - 15) = 0
(x - 15)(x - 20) = 0
x = 15, 20
If x = 15, then y = 70 - 2x = 70 - 30 = 40
If x = 20, then y = 70 - 2x = 70 - 40 = 30
Thus, the length of the shorter side is 15 m when the longer side is 40 m. The length of the shorter side is 20 m when the longer side is 30 m.
Solution 12
Let the side of the square lawn be x m.
Area of the square lawn = x2 m2
The square lawn is bounded on three sides by a path which is 4 m wide.
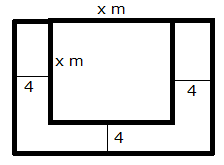
Area of outer rectangle = (x + 4) (x + 8) = x2 + 12x + 32
Area of path = x2 + 12x + 32 - x2 = 12x + 32
From the given information, we have:
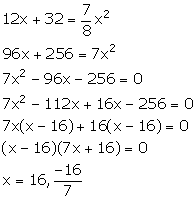
Since, x cannot be negative. So, x = 16 m.
Thus, each side of the square lawn is 16 m.
Solution 13
Let the original length and breadth of the rectangular room be x m and y m respectively.
Area of the rectangular room = xy = 300
![]()
New length = (x - 5) m
New breadth = (y + 5) m
New area = (x - 5) (y + 5) = 300 (given)
Using (1), we have:
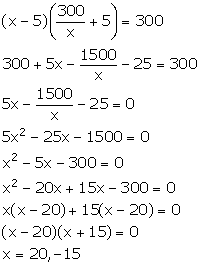
But, x cannot be negative. So, x = 20.
Thus, the length of the room is 20 m.
Solving (simple) Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Exercise Ex. 6(C)
Solution 1
(i) Speed of ordinary train = x km/hr
Speed of express train = (x + 25) km/hr
Distance = 300 km
We know:
![]()
![]() Time taken by
ordinary train to cover 300 km =
Time taken by
ordinary train to cover 300 km = ![]()
Time
taken by express train to cover 300 km = ![]()
(ii) Given that the ordinary train takes 2 hours more than the express train to cover the distance.
Therefore,
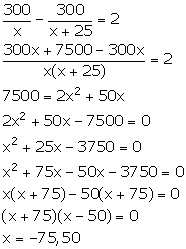
But, speed cannot be negative. So, x = 50.
![]() Speed of the
express train = (x + 25) km/hr = 75 km/hr
Speed of the
express train = (x + 25) km/hr = 75 km/hr
Solution 2
Let the speed of the car be x km/hr.
Distance = 36 km
Time taken to cover a distance of 36 km = ![]()
![]()
New speed of the car = (x + 10) km/hr
New time taken by the car to cover a distance of 36 km = ![]()
From the given information, we have:
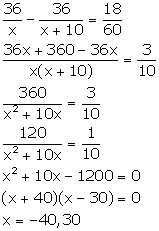
But, speed cannot be negative.
So, x = 30.
Hence, the original speed of the car is 30 km/hr.
Solution 3
Let the original speed of the aeroplane be x km/hr.
Time
taken to cover a distance of 1200 km = ![]()
![]()
Let the new speed of the aeroplane be (x - 40) km/hr.
Time
taken to cover a distance of 1200 km = ![]()
From the given information, we have:
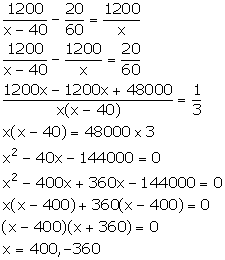
But, speed cannot be negative. So, x = 400.
Thus, the original speed of the aeroplane is 400 km/hr.
Solution 4
Let x km/h be the original speed of the car.
We know that,
![]()
It is given that the car covers a distance of 400 km with the speed of x km/h.
Thus, the time taken by the car to complete 400 km is
![]()
Now, the speed is increased by 12 km.
![]()
Also given that, increasing the speed of the car will decrease the time taken by 1 hour 40 minutes.
Hence,
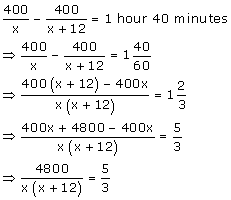
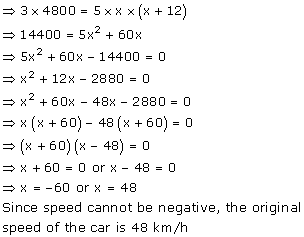
Solution 5
We know:
![]()
Given, the girl covers a distance of 6 km at a speed x km/ hr.
Time
taken to cover first 6 km = ![]()
Also, the girl covers the remaining 6 km distance at a speed (x + 2) km/ hr.
Time
taken to cover next 6 km = ![]()
Total
time taken to cover the whole distance = 2 hrs 30 mins = ![]()
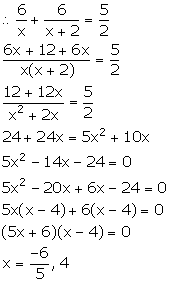
Since, speed cannot be negative. Therefore, x = 4.
Solution 6
Let the original speed of the car be y km/hr.
We know:
![]()
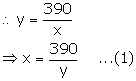
New speed of the car = (y + 4) km/hr
New
time taken by the car to cover 390 km = ![]()
From the given information,
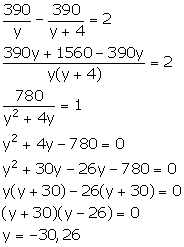
Since, time cannot be negative, so y = 26.
From (1), we have:
![]()
Solution 7
Let the speed of goods train be x km/hr. So, the speed of express train will be (x + 20) km/hr.
Distance = 1040 km
We know:
![]()
Time taken by goods train to cover a distance of 1040 km = ![]()
Time taken by express train to cover a distance of 1040 km = ![]()
It is given that the express train arrives at a station 36 minutes before the goods train. Also, the express train leaves the station 2 hours after the goods train. This means that the express train arrives at the station ![]() before the goods train.
before the goods train.
Therefore, we have:
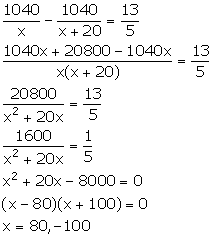
Since, the speed cannot be negative. So, x = 80.
Thus, the speed of goods train is 80 km/hr and the speed of express train is 100 km/hr.
Solution 8
C.P. of the article = Rs x
S.P. of the article = Rs 16
Loss = Rs (x - 16)
We know:
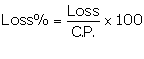
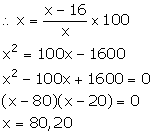
Thus, the cost price of the article is Rs 20 or Rs 80.
Solution 9
C.P. of the article = Rs x
S.P. of the article = Rs 52
Profit = Rs (52 - x)
We know:
![]()
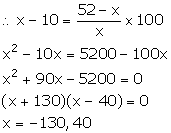
Since, C.P. cannot be negative. So, x = 40.
Thus, the cost price of the article is Rs 40.
Solution 10
Let the C.P. of the chair be Rs x
S.P. of chair = Rs 75
Profit = Rs (75 - x)
We know:
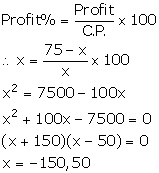
But, C.P. cannot be negative. So, x = 50.
Hence, the cost of the chair is Rs 50.
Solving (simple) Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Exercise Ex. 6(D)
Solution 1
From the given information, we have:
n(n + 2) = 168
n2 + 2n - 168 = 0
n2 + 14n - 12n - 168 = 0
n(n + 14) - 12(n + 14) = 0
(n + 14) (n - 12) = 0
n = -14, 12
But, n cannot be negative.
Therefore, n = 12.
Solution 2
From the given information,
16t2 + 4t = 420
4t2 + t - 105 = 0
4t2 - 20t + 21t - 105 = 0
4t(t - 5) + 21(t - 5) = 0
(4t + 21)(t - 5) = 0
t
= ![]() , 5
, 5
But, time cannot be negative.
Thus, the required time taken is 5 seconds.
Solution 3
Let the ten's and unit's digit of the required number be x and y respectively.
From the given information,
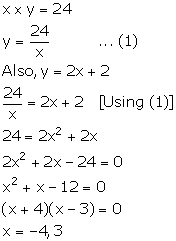
The digit of a number cannot be negative, so, x = 3.
![]()
Thus, the required number is 38.
Solution 4
The ages of two sisters are 11 years and 14 years.
Let in x number of years the product of their ages be 304.
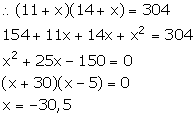
But, the number of years cannot be negative. So, x = 5.
Hence, the required number of years is 5 years.
Solution 5
Let the present age of the son be x years.
![]() Present age of
man = x2 years
Present age of
man = x2 years
One year ago,
Son's age = (x - 1) years
Man's age = (x2 - 1) years
It is given that one year ago; a man was 8 times as old as his son.
![]() (x2
- 1) = 8(x - 1)
(x2
- 1) = 8(x - 1)
x2 - 8x - 1 + 8 = 0
x2 - 8x + 7 = 0
(x - 7) (x - 1) = 0
x = 7, 1
If x = 1, then x2 = 1, which is not possible as father's age cannot be equal to son's age.
So, x = 7.
Present age of son = x years = 7 years
Present age of man = x2 years = 49 years
Solution 6
Let the present age of the son be x years.
![]() Present age of
father = 2x2 years
Present age of
father = 2x2 years
Eight years hence,
Son's age = (x + 8) years
Father's age = (2x2 + 8) years
It is given that eight years hence, the age of the father will be 4 years more than three times the age of the son.
![]() 2x2
+ 8 = 3(x + 8) +4
2x2
+ 8 = 3(x + 8) +4
2x2 + 8 = 3x + 24 +4
2x2 - 3x - 20 = 0
2x2 - 8x + 5x - 20 = 0
2x(x - 4) + 5(x - 4) = 0
(x - 4) (2x + 5) = 0
x
= 4, ![]()
But, the age cannot be negative, so, x = 4.
![]() Present age of
son = 4 years
Present age of
son = 4 years
Present age of father = 2(4)2 years = 32 years
Solution 7
Let the speed of the stream be x km/hr.
![]() Speed of the
boat downstream = (15 + x) km/hr
Speed of the
boat downstream = (15 + x) km/hr
Speed of the boat upstream = (15 - x) km/hr
Time
taken to go 30 km downstream = ![]()
Time
taken to come back = ![]()
From the given information,
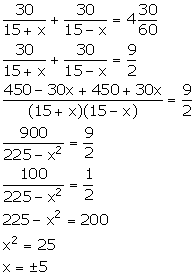
But, x cannot be negative, so, x = 5.
Thus, the speed of the stream is 5 km/hr.
Solution 8
Number of oranges = y
Cost of one orange =![]()
The servant ate 3 oranges, so Mr. Mehra received (y - 3) oranges.
So, x = y - 3 ![]() y = x + 3 ...(1)
y = x + 3 ...(1)
Cost of one orange paid by Mr. Mehra = ![]()
=![]()
Now, Mr. Mehra pays a total of Rs 15.
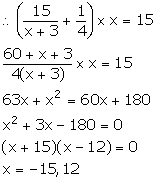
But, the number of oranges cannot be negative. So, x = 12.
Solution 9
Let the number of children be x.
It is given that Rs 250 is divided amongst x students.
So, money received by each child = Rs![]()
If there were 25 children more, then
Money received by each child = Rs![]()
From the given information,
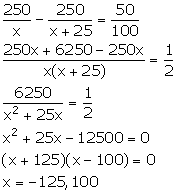
Since, the number of students cannot be negative, so, x = 100.
Hence, the number of students is 100.
Solution 10
Original weekly wage of each worker = Rs x
Original weekly wage bill of employer = Rs 3150
Number
of workers = ![]()
New weekly wage of each worker = Rs (x + 5)
New weekly wage bill of employer = Rs 3250
Number
of workers = ![]()
From the given condition,
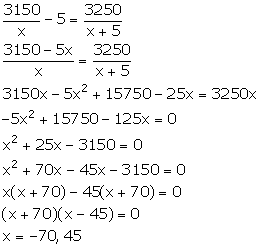
Since, wage cannot be negative, x = 45.
Thus, the original weekly wage of each worker is Rs 45.
Solution 11
Number of articles bought by the trader = x
It is given that the trader bought the articles for Rs. 1200.
So, cost of one article = Rs.![]()
Ten articles were damaged. So, number of articles left = x - 10
Selling price of each of (x - 10) articles = Rs.![]()
Selling price of (x - 10) articles = Rs. (x - 10) ![]()
Profit = Rs. 60
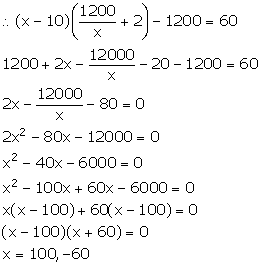
Number of articles cannot be negative. So, x = 100.
Solution 12
Let the number of articles bought be x.
Total cost price of x articles = Rs 4800
Cost
price of one article = Rs![]()
Selling price of each article = Rs 100
Selling price of x articles = Rs 100x
Given, Profit = C.P. of 15 articles
![]() 100x - 4800 =
15
100x - 4800 =
15 ![]()
100x2
- 4800x = 15 ![]() 4800
4800
x2 - 48x - 720 = 0
x2 - 60x + 12x - 720 = 0
x(x - 60) + 12(x - 60) = 0
(x - 60) (x + 12) = 0
x = 60, -12
Since, number of articles cannot be negative. So, x = 60.
Thus, the number of articles bought is 60.
Solving (simple) Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Exercise Ex. 6(E)
Solution 1

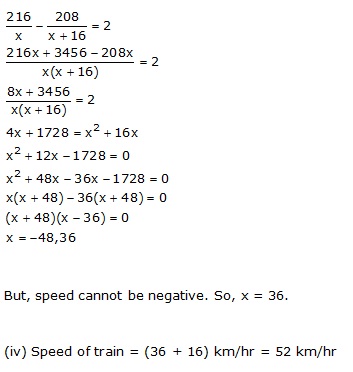
Solution 2

Solution 3
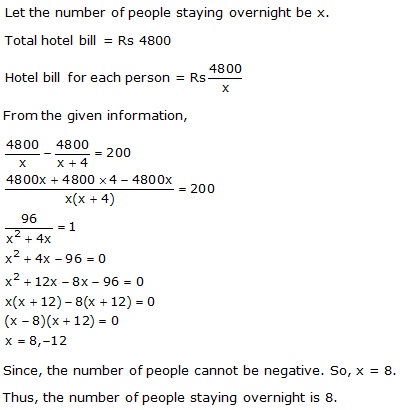
Solution 4


Solution 5
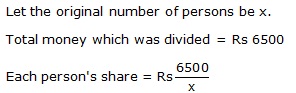

Solution 6

Solution 7


Solution 8
S = n(n + 1)
Given, S = 420
n(n + 1) = 420
n2 + n - 420 = 0
n2 + 21n - 20n - 420 = 0
n(n + 21) - 20(n + 21) = 0
(n + 21) (n - 20) = 0
n = -21, 20
Since, n cannot be negative.
Hence, n = 20.
Solution 9
Let the present ages of father and his son be x years and (45 - x) years respectively.
Five years ago,
Father's age = (x - 5) years
Son's age = (45 - x - 5) years = (40 - x) years
From the given information, we have:
(x - 5) (40 - x) = 124
40x - x2 - 200 + 5x = 124
x2 - 45x +324 = 0
x2 - 36x - 9x +324 = 0
x(x - 36) - 9(x - 36) = 0
(x - 36) (x - 9) = 0
x = 36, 9
If x = 9,
Father's age = 9 years, Son's age = (45 - x) = 36 years
This is not possible.
Hence, x = 36
Father's age = 36 years
Son's age = (45 - 36) years = 9 years
Solution 10
Let the number of rows in the original arrangement be x.
Then, the number of seats in each row in original arrangement = x
Total number of seats =![]()
From the given information,
2x(x - 10) = x2 + 300
2x2 - 20x = x2 + 300
x2 - 20x - 300 = 0
(x - 30) (x + 10) = 0
x = 30, -10
Since, the number of rows or seats cannot be negative. So, x = 30.
(i) The number of rows in the originalarrangement = x = 30
(ii) The number of seats after re-arrangement = x2 + 300 = 900 + 300 = 1200
Solution 11

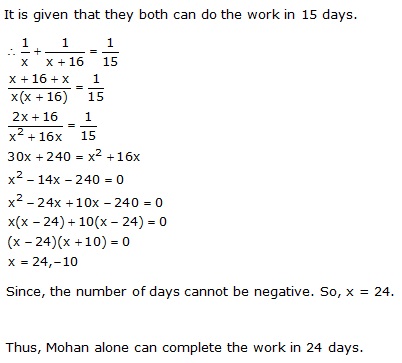
Solution 12
Let the age of son 2 years ago be x years.
Then, father's age 2 years ago = 3x2 years
Present age of son = (x + 2) years
Present age of father = (3x2 + 2) years
3 years hence:
Son's age = (x + 2 + 3) years = (x + 5) years
Father's age = (3x2 + 2 + 3) years = (3x2 + 5) years
From the given information,
3x2 + 5 = 4(x + 5)
3x2 - 4x - 15 = 0
3x2 - 9x + 5x - 15 = 0
3x(x - 3) + 5(x - 3) = 0
(x - 3) (3x + 5) = 0
x = 3,
Since, age cannot be negative. So, x = 3.
Present age of son = (x + 2) years = 5 years
Present age of father = (3x2 + 2) years = 29 years
Solution 13

Solution 14
Given, the difference between two digits is 6 and the ten's digit is bigger than the unit's digit.
So, let the unit's digit be x and ten's digit be (x + 6).
From the given condition, we have:
x(x + 6) = 27
x2 + 6x - 27 = 0
x2 + 9x - 3x - 27 = 0
x(x + 9) - 3(x + 9) = 0
(x + 9) (x - 3) = 0
x = -9, 3
Since, the digits of a number cannot be negative. So, x = 3.
Unit's digit = 3
Ten's digit = 9
Thus, the number is 93.
Solution 15


Solution 16

Solution 17
Time taken by bus
to cover total distance with speed x km/h = ![]()
Time taken by bus
to cover total distance with speed (x - 10) km/h = ![]()
According to the given condition, we have
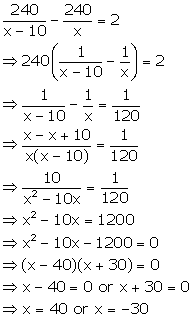
Since the speed cannot be negative, we have x = 40 km/h
Solution 18
Given that he sum of the ages of Vivek and his younger brother Amit is 47 years.
Let the age of Vivek = x
⇒ the age of Amit = 47 - x
The product of their ages in years is 550 …. given
⇒ x(47 - x) = 550
⇒ 47x - x2 = 550
⇒ x2 - 47x + 550 = 0
⇒ x2 - 25x - 22x + 550 = 0
⇒ x(x - 25) - 22(x - 25) = 0
⇒ (x - 25) (x - 22) = 0
⇒ x = 25 or x = 22
Given that Vivek is an elder brother.
∴ x = 25 years = age of Vivek and
age of Amit = 47 - 25 = 22 years

